Lap KPIs
The lap KPIs (key performance indicators) feature in HH Data Management enables logged data to be analysed based on user-defined math expressions. To use the lap KPI feature, first the math expressions are defined using the data analysis profile. Then the logged data is associated to the runsheets. Once these two tasks have been completed the KPIs can be calculated. Once the KPIs are calculated the results are stored in the HH Data Management database and can be analysed using the main graph or the results exported using the data export features.
The logged data is added to the runsheets using attached files. The KPI calculations are performed on the server, this makes it quick and easy to recalculate the KPIs at any time after an event. For example, as the season evolves more KPIs may be developed and the KPI implementation allows for updating the calculated results for all past events if desired.
Data analysis profile
The data analysis profile view can be accessed from the admin tab of the ribbon bar:
The data analysis profile view will open:
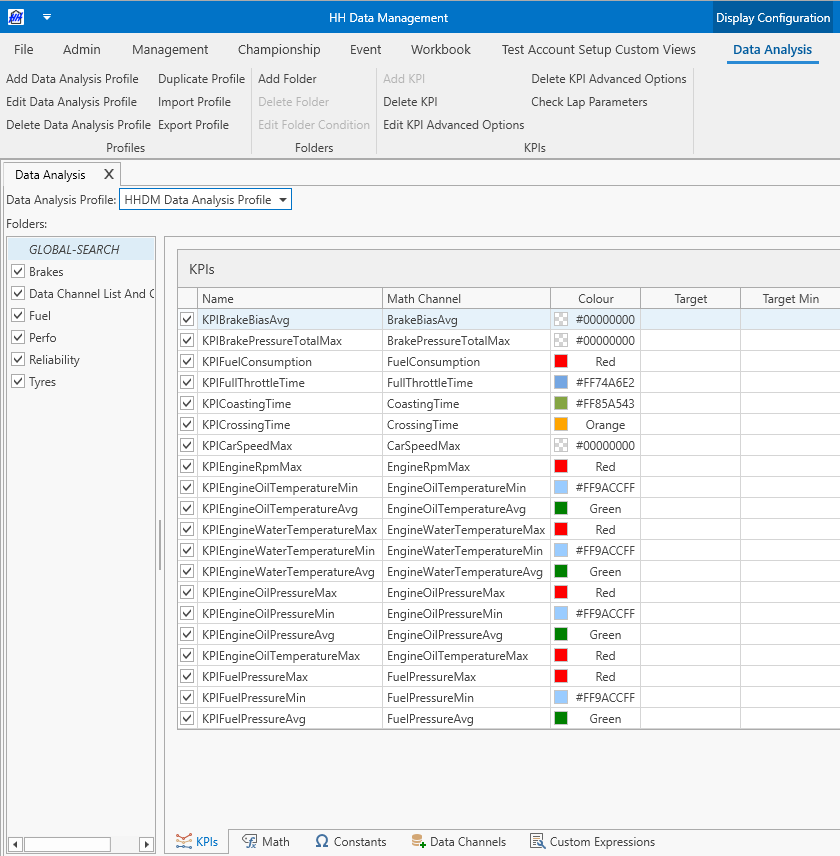
The following items exist within the data analysis profile once it is created:
- Folders
- KPIs
- Math channels
- Constants
- Data channels
- Data channel aliases
- Custom expressions
All items are created, edited and deleted using the buttons on the ribbon bar. The items will be presented in their logical order, not in the order of the tabs in the software.
All items have checkboxes beside their definitions. These checkboxes allow the items to be disabled, meaning that they will not be included in a KPI calculation. For example if a folder is unchecked then any KPIs, math channels, constants, data channels or custom expressions defined in this folder will not be calculated.
Folders
Folders are purely an organizational construct and do not affect the functionality in any way. Items created within one folder can be referenced from another folder.
The GLOBAL-SEARCH folder is an automatically added item in the folder list that shows the items from all folders in the tables all at once. New items cannot be added when the GLOBAL-SEARCH folder is selected.
Folder conditions
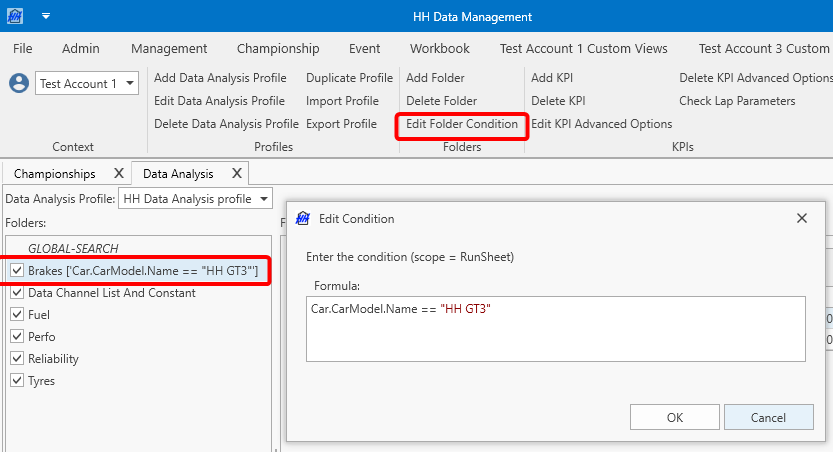
Folders can be taken into account based on conditions. Selecting a folder and clicking the "Edit Folder Condition" button allows to add/edit a folder condition. Only when this condition is met, all the KPIs in this folder will get calculated. This is helpful if some KPIs should get only calculated if for example certain sensors are installed in the car, or it's possible to have different KPIs for different cars in the same event or for different sessions. The scope for the formula is always the current runsheet. To remove a folder condition the formula needs to be cleared.
Data channels & data channel aliases
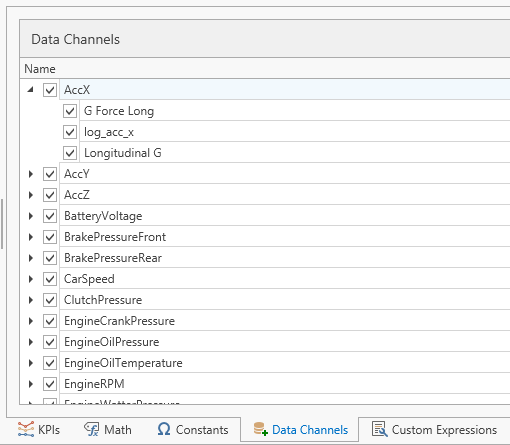
The data channel concept is used to define the channels that are available in the data file. Technically, these are not required, but they are helpful as it enables the intellisense to work when writing math channels, and it allows aliasing if a channel could have different names in different files. There are two levels; the data channel and then as children the data channel alias. The data channel is the name that will be used in HH Data Management to reference this channel, and if no aliases exist, then this name will also be the name that is searched for in the data file to locate the channel data. Data channel aliases can be used to support cases where data might have different names in different files, or simply to change the name between the data file and HH Data Management. This may be necessary if the channel name in the data file doesn't conform to the HH Data Management syntax requirements. For example, HH Data Management doesn't allow spaces in channel names, where as a lot of data logger systems do. When processing the KPIs, HH Data Management will first search for the channel using the data channel name, then iterate through the data channel aliases, in the order they appear in the tree, to find the data. To change the priority the data channel aliases are given, drag the alias to the desired position in the list. In the example screenshot, for the AccX channel, the search order would be:
- AccX
- G Force Long
- log_acc_x
- Longitudinal G
Constants
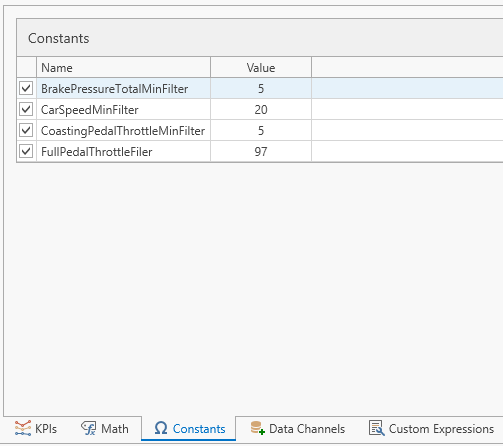
The constants are used to define constant values that can be used in math channels along with data channels.
Custom expressions

One of the key points of HH Data Management is that all data is stored in a single place and this should in theory make it possible to access all relevant information about the car for each lap. For example, when running KPIs, part specifications (e.g. spring rates) and sensor offsets stored in the setup sheet or runsheet should be accessible in the math expressions. This link between the KPI system and the rest of HH Data Management is accomplished using the custom expressions. It is not possible to access the HH Data Management parameters directly in a math channel expression because there are two separate languages in HH Data Management; the KPI expression language and the math expression language and the two are not interchangeable. This is an intentional decision as the two languages are designed to accomplish two very different tasks.
When writing a custom expression the math expression language is used, in the same way it is used when making a math parameter in a definition or defining an export parameter in a data export.
When creating or editing a custom expression, a window will pop-up:
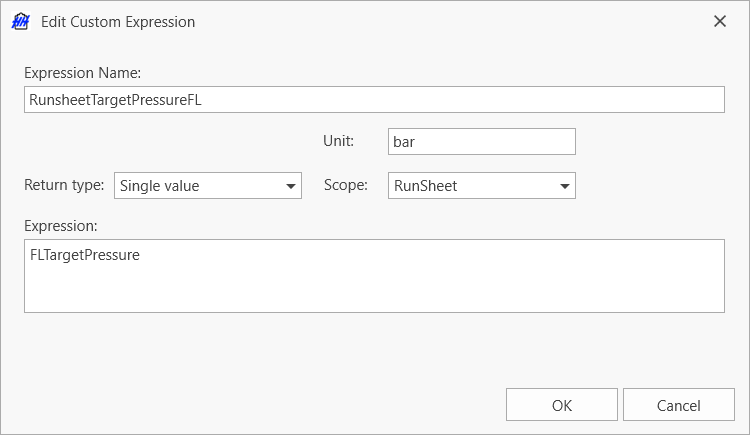
The expression name is the name that should be used when referencing this custom expression in a KPI math channel. See the single vs multiple value return types section for an explanation of the return type combobox. The scope combobox has two options; runsheet or lap. This sets the scope that the math expression can be written about. Normally this should be set to runsheet (to get setup-related information). But if the expression needs to return some info from the lap (perhaps to get fuel remaining), then the scope should be changed to lap. The unit allows the return unit of the math expression to be defined.
The scope also has a minor impact on the performance of the custom expression getting evaluated. If the lap scope is selected then the expression has to be evaluated for each lap, but if the runsheet scope is selected then the expression is only evaluated once per run.
Math channels
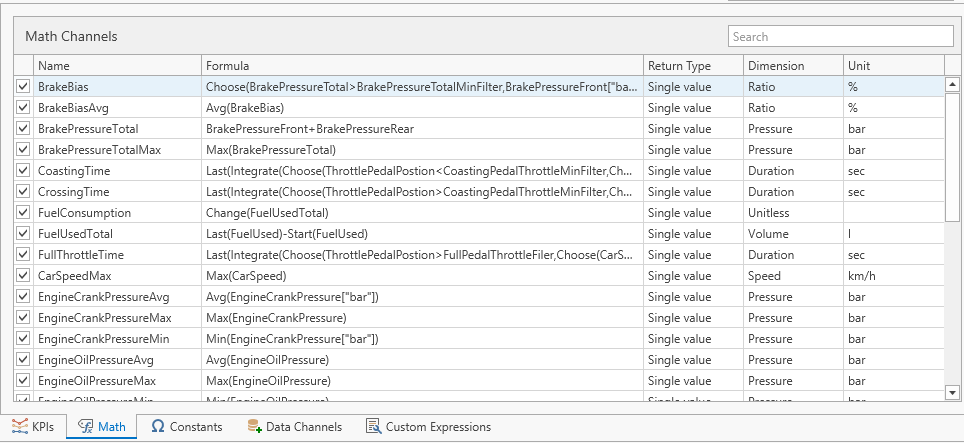
The math channels are where the actual math for the KPIs are defined. Math channels can reference data channels, constants or custom expressions. For more information on the language used to write math channels and the functions available, please refer to the KPI expression reference section.
When creating or editing a math channel, a window will pop-up:
The return dimension and unit can be specified here.
As mentioned in the data channel section, if a channel name is used in a math expression, but not defined in the list of data channels or data channel aliases, then HH Data Management will still search the data file for a channel with this name. The channel name will be underlined in green as a notification that this is a channel name that is unknown to HH Data Management:
KPIs
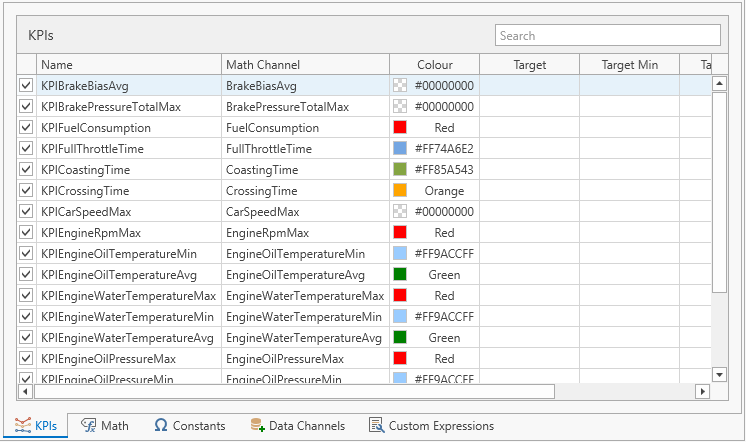
The KPIs are the final part of defining how a lap KPI is calculated.
Name
The name is the final name of the lap KPI parameter that will be used to store the result in HH Data Management. Therefore, the value entered for the name of the KPI must match an existing parameter on the lap definition of the appropriate type. If this isn't the case, then the KPI result will not get saved to the database.
The check lap parameter button on the ribbon can be used to automatically scan the lap definition to make sure that all required parameters exist and will give an option to automatically create them if they do not exist.
Math channel
The math channel drop down allows the math channel that will be used to calculate the result for this KPI to be selected.
Advanced options
Selecting a row in the KPI table and then clicking the edit KPI advanced options will open a popup window:
When KPIs are calculated in HH Data Management, each lap is considered individually (and then mapped back to the laps in the database for storing the results). The advanced options allows for additional data to be loaded when the data is processed. Data from before or after the current lap can be loaded by enabling the options. This can be useful for example if calculating a straight line KPI that needs to consider the full S/F straight.
The delete KPI advanced options button can be used to remove the options for the selected KPI and reset all values back to their default.
Single vs multiple value return types
When defining math channels the return type can be specified as either single or multiple. Most standard KPIs will be single, for example, a KPI that calculates the max speed of the lap, or the % of the lap spent on full throttle. A single value per lap is generated. However, KPIs can be created that calculate multiple values per lap using gates, for example, the time spent in each corner, or the minimum speed for each corner. When a KPI is defined as having a single return type it is stored in a double parameter on the lap definition, and the name of the KPI must match the name of the lap double parameter. When a KPI is defined as having a multiple return type it is stored in a collection parameter on the lap definition. This collection then has an item for each KPI value, and the calculated value is stored in a double parameter on the lap collection item definition. When specifying the name for the KPI, it should be specified as <lap collection parameter name>.<lap collection item double parameter>, for example Corners.vMin, where Corners is a collection on the lap definition and vMin is a double parameter on the lap collection item definition.
To create a multiple value KPI custom expressions must be used, and this custom expression must return a list of double values. This will force all KPIs that reference this custom expression to have a return type of multiple. Generally, these custom expressions will reference a collection parameter and use the Select function to extract a double parameter and return a list of double values. For example, a collection could be made on the track configuration definition with parameters that allow the start and end distances or GPS coordinates of each corner to be defined. Two custom expressions could then be created to get these start and end values.
| Single | Multiple |
|---|---|
| Single value per lap | Multiple values per lap |
| Stored in a double parameter on the lap definition | Stored in a collection parameter on the lap definition, in a double parameter on the lap collection item definition |
| KPI name should match name of lap double parameter | KPI name should match <lap collection parameter name>.<lap collection item double parameter> |
Using the KPIs in an event
There are two tasks that must be carried out for each event and car to be able to run the KPIs:
- define which data analysis profile should be used
- add the files to the runsheet
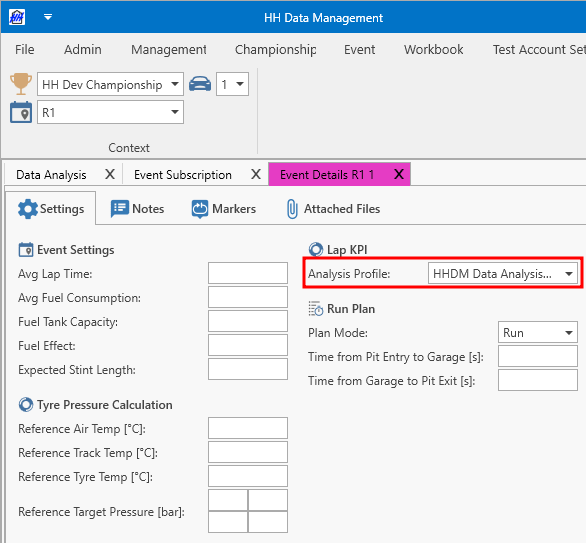
Selecting the data analysis profile
The data analysis profile to be used for each event/car is selected in the event data view.
Runsheet KPI Management view
The data files for each run are managed using the runsheet KPI management view that can be opened from the event tab of the ribbon bar:
The runsheet KPI management view will open:
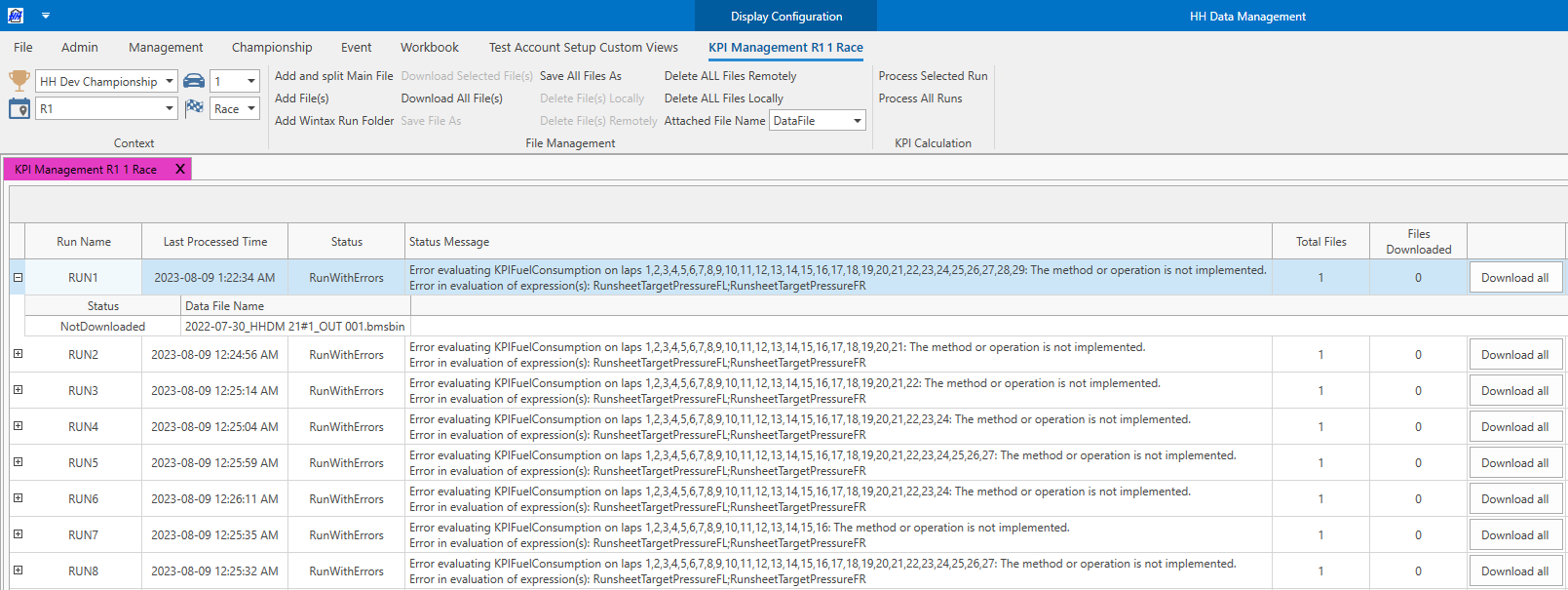
The table on the view shows a row for each run for the selected car and session. The following information is shown in the table:
- Lap Offset: the offset to apply when reading laps from the data file to link them to the lap in HH Data Management. If the value is empty or 0 then no offset is applied. As an example, a value of 1 will skip the first lap in the data file and write results from the second lap in the data file to the first lap in HH Data Management.
- Last Processed Time: the last time the KPIs were processed for this run
- Status: the status of the KPI calculation. Possible values are:
- NotRun: the KPIs have not been calculated for this run
- Run: the KPIs have been calculated successfully for this run
- RunWithErrors: the KPIs have been calculated for this run, but some errors were encountered
- Failed: the KPIs have failed to run due to an error. Please retry to run them and if the error persists contact support@hh-dev.com and report the issue.
- Started: the KPI calculation is currently running and the results should be available shortly
- Queued: the request to run the KPI calculation has been sent to the server and should start soon
- Status Message: this column is useful if the status of the KPIs are RunWithErrors or Failed. More information is provided to explain the issues that were encountered.
- Total Files: the number of files attached to the run. Some data systems can export one file per lap, meaning that multiple files have to be attached to the runsheet.
- Files Downloaded: the number of files that have been downloaded and stored locally on the computer
- The Download all button can be used to download all attached files of the current run to the local computer
Each row can be expanded to show all files that are attached to the current run.
In this example, the KPIs have run successfully, but there have been some errors:
- the
KPIFuelConsumptionfailed to run - in this case the expression should be checked for errors - the custom expressions
RunsheetTargetPressureFLandRunsheetTargetPressureFRboth failed to evaluate, so they should also be checked for errors
Adding files
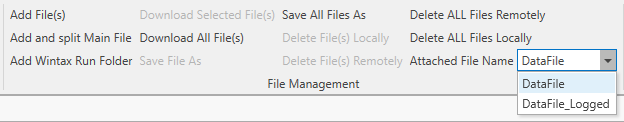
There are three options available when adding files to the run:
- Add file(s): this button allows one or multiple files to be added to the run that is currently selected in the table.
- Add and split main file: this button allows a single file to be selected and split into parts and added to multiple runs (see below for a full explanation)
- Add Wintax run folder: this button allows a Wintax run folder to be uploaded to HH Data Management. To simplify the process of adding this type of data to the runsheet the contents of the folder will be zipped into a file with extension *.hhrunwtx.
By default, adding the data files to the runsheet is a manual process, but it can be automated using a plugin depending on the workflow each team uses.
The KPI calculation will automatically run for each run once all files have finished uploading.
Add and split main file
This function is currently only supported for Motec and Pi files.
After clicking the Add and split main file button the following window will open:
Click the Select file button and select the data file that is to be imported. Each run will from the session will be shown in the table. Select the runs for the file by typing the file lap numbers into the rows. In the example screenshot, the file will be split between laps 10 and 11 (based on the lap number in the file), two files will be created and they will be added to runs 2 and 3.
File management
The remaining buttons on the ribbon bar are used to manage the attached files.
- Download selected file(s): downloads the selected files to the local computer
- Download all file(s): downloads all files from all runs for the current car and session to the local computer
- Save file as: allows the selected file to be exported from HH Data Management and saved in an accessible location on the local computer (so it can be used in an external application)
- Save all file as: saves all files from all runs for the current car and session to the selected directory. Existing files with the same name in the target directory will NOT be overwritten.
- Delete file(s) locally: deletes the selected files from the local computer
- Delete file(s) remotely: deletes the selected files from the server and the local computer (this is permanent and affects all users)
- Delete ALL file(s) locally: deletes all files from all runs for the current car and session from the local computer
- Delete ALL file(s) remotely: deletes all files from all runs for the current car and session from the server and the local computer (this is permanent and affects all users)
Running calculations
The KPI calculations can be triggered manually using the Process selected run and Process all runs buttons on the ribbon bar. The Process all runs button will trigger the KPI calculation for all runs for the current car and session.
KPI calculation
Once everything is set up properly the KPI calculation can finally run. The KPI calculator runs on the HH Data Management server. The server is responsible for getting the correct data analysis profile, getting the data file(s) from the runsheet, and then calculating all the KPI values, and finally writing the results back to the HH Data Management system (which then distributes the results to all users). The alignment between the laps in the data file and the laps in HH Data Management is managed by the server and simply aligns them one-to-one, i.e. the results from the first lap in the data file will be written to the first lap in HH Data Management.
The KPI calculator is designed to be able to handle large amounts of processing requests, therefore it is possible to calculate multiple KPIs at the same time (e.g. recalculating the full season of KPIs). However, at times of high load there may be a longer than normal wait, for the results to become available.
Multiple data sets
HH Data Management is capable of handling multiple data sets, for example telemetry data and logged data, or data sets from multiple loggers. This is done by using multiple attached file parameters in the software.
Furthermore, it is also possible to:
- use a different data analysis profile between each data set
- map the names of the parameters that the results are stored in
Adding support for an additional data set
By default all HH Data Management accounts come configured to use the DataFile attached file parameter for the KPIs. When adding a second data source the name of the new attached file parameter must start with DataFile_. For example, a new parameter called DataFile_Logged could be created. Note that it is important to select Allow multiple files when creating this attached file parameter.
Furthermore, to see the status for the KPIs run against this data set, the following parameters should be created on the run sheet definition:
DataFile_<data set name>_KpiStatuswith type doubleDataFile_<data set name>_LastKpiProcessedTimewith type datetimeDataFile_<data set name>_KpiAnalysisFeedbackwith type textDataFile_<data set name>_KpiLapOffsetwith type double
In the KPI management view, there is a combobox on the ribbon bar that controls which attached file parameter is being controlled in the view.
A parameter called DefaultKpiAttachedFileName can be created in the AccountOptions definition. If this parameter exists, an option will appear allowing the default attached file parameter that is used in the KPI management view to be defined.
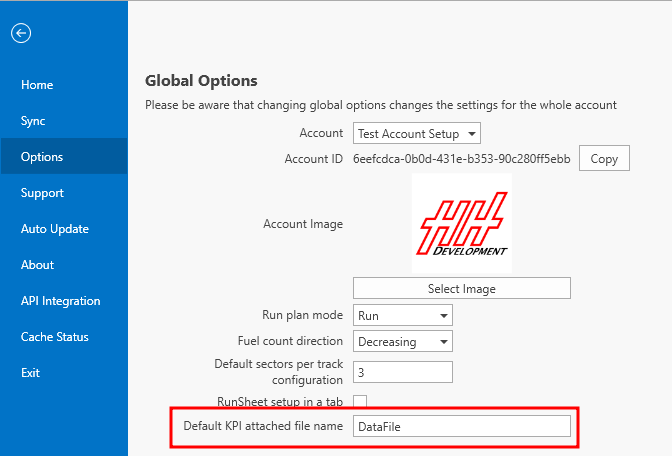
This controls the attached file parameter that will be selected by default when a new KPI management view is opened.
Note that HH Data Management needs to be restarted after adding the parameter to see the field appear in the backstage.
Changing data analysis profile
To use a different data analysis profile for each data set, a parameter must be created in the EventCar definition with the name format DataFile_<data set name>_DataAnalysisProfileId (e.g. DataFile_Logged_DataAnalysisProfileId). If this parameter is set then that specified data analysis profile will be used. In the follow section a custom view is created that allows this value to be set. If this parameter is not created or not set then the default data analysis profile will be used for the data set.
Mapping parameter names
It is also possible to map the parameter names that will be used to save the KPI results. This is useful if there are two data sets that can use a common data analysis profile, but the results should be stored in different parameters. This might be useful if there are telemetry and logged data sets. The math is the same between the data sets but both result sets should be saved (for example so the KPI calculated from the telemetry data can be compared with the KPI coming from the logged data). Creating a separate data analysis profile with the same math but different KPI names would be a large amount of unnecessary work. The KPIs coming from the logged data could be stored in parameters ending with _Logged. For example, vMax vs vMax_Logged.
To accomplish this a parameter must be created in the EventCar definition with the name format DataFile_<data set name>_KpiParameterNamePattern (e.g. DataFile_Logged_KpiParameterNamePattern). The syntax for this value is that the character is used to define the original name and any additional text is added to the target parameter name. For example, `_Loggedwould append_Logged` onto all of the parameter names.
Note that these parameters must exist in the account and the data can only be referenced using the mapped name.
In the follow section a custom view is created that allows this value to be set. If this parameter is not created or not set then the KPI parameter names will not be mapped.
Creating a custom view
These new parameters need to be set by the user and this can be set up using a single table custom view along with a column profile.
In this example, the following are assumed:
- Run sheet attached file parameter name:
DataFile_Logged - KPI mapping: for the
DataFile_Loggedfiles,_Loggedwill be appended to the end of all KPI parameters
Columns
A column profile linked to the EventCar definition should be created.
A column should be created to show the car number:
- Column Type: Text
- Field Name:
Car.Strings.Number
Next, columns must be created for each additional data set and feature that is to be used. The column for the custom data analysis profile should be:
- Column Type: Combobox
- Field Name:
Strings.DataFile_Logged_DataAnalysisProfileId - Items Source Binding Path:
ContextSelection.SelectedManagementCache.DataAnalysisProfileCache.DataAnalysisProfiles - Display Member Path:
Strings.Name - Value Member Path:
Id
The column for the KPI parameter mapping should be:
- Column Type: Parameter
- Linked Parameter:
DataFile_Logged_KpiParameterNamePattern
Custom view
A custom view should be created with the following settings:
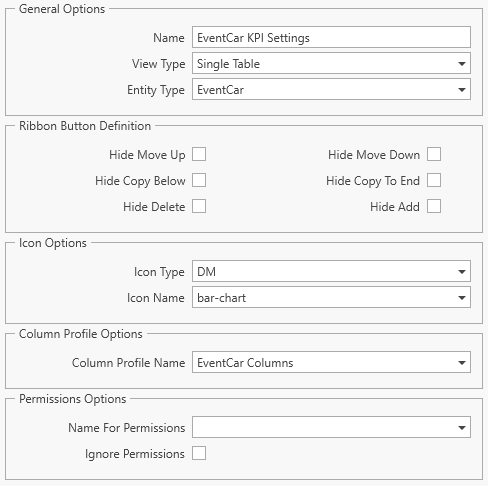
This will give a table with the following appearance:
That allows the data analysis profile and KPI parameter name mapping to be defined.
Remember that these additional parameters are not necessary and should only be created and defined if this functionality is required. To keep using the default data analysis profile selection and not change the parameter names that KPIs are written to, no changes are required beyond creating the additional attached file parameter.